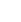EFFECTIVE PRESSURE AND GENERALIZED EFFECTIVE BIOT STRESS OF POROUS CONTINUUM IN UNSATURATED GRANULAR MATERIALS
-
摘要:多孔连续体理论框架下的非饱和多孔介质广义有效压力定义和Bishop参数的定量表达式长期以来存在争议, 这也影响了对与其直接相关联的非饱和多孔介质广义Biot有效应力的正确预测. 基于随时间演变的离散固体颗粒−双联液桥−液膜体系描述的Voronoi胞元模型, 利用由模型获得的非饱和颗粒材料表征元中水力-力学介观结构和响应信息, 文章定义了低饱和度多孔介质局部材料点的有效内状态变量: 非饱和多孔连续体的广义Biot有效应力和有效压力, 导出了其表达式. 所导出的有效压力公式表明, 非饱和多孔连续体的有效压力张量为各向异性, 它不仅对非饱和多孔连续体广义Biot有效应力张量的静水应力分量的影响呈各向异性, 同时也对其剪切应力分量有影响. 文章表明, 非饱和多孔连续体中提出的广义Biot理论和双变量理论的基本缺陷在于它们均假定反映非混和两相孔隙流体对固相骨架水力−力学效应的有效压力张量为各向同性. 此外, 为定义各向同性有效压力张量和作为加权系数而引入的Bishop参数并不包含对非饱和多孔连续体中局部材料点水力−力学响应具有十分重要效应的基质吸力. 所导出的非饱和多孔介质广义Biot有效应力和有效压力公式(包括反映有效压力各向同性效应的有效Bishop参数)可在以协同计算均匀化方法为代表的非饱和颗粒材料计算多尺度方法中上传到在宏观非饱和多孔连续体设置了表征元的局部材料点.Abstract:The definition of effective pressure with associated formula of the Bishop parameter for unsaturated porous medium proposed in the frame of the theory of macroscopic porous continuum has been controversial for a long time. This also affects the correct prediction of directly related generalized Biot effective stress. Based on the Voronoi cell model described with the discrete system composed of solid particles, binary bond liquid bridges and liquid films, the present paper presents the definitions of effective internal state variables at local material points in unsaturated porous continua with low saturation, i.e. effective pressure and generalized Biot effective stress. Using the proposed Voronoi cell model, their expressions are formulated with the information of hydro-mechanical meso-structure and moso-response evolved with incremental loading process exerted on the representative volume element (RVE) of unsaturated granular material. With the derived effective pressure formula, it is demonstrated that the effective pressure tensor of unsaturated porous continuum is anisotropic. It has not only an anisotropic effect on hydrostatic components, but also an effect on shear stress components, of generalized Biot effective stress tensor. It is demonstrated that the fundamental defect of both the generalized Biot theory and the so-called bivariate theory lies in that it is assumed that effective pore pressure tensor representing the hydro-mechanical effect of two immiscible pore fluids on the solid skeleton of unsaturated porous continua is isotropic. In addition, the Bishop parameter introduced as the weighted factor to define the isotropic effective pore pressure tensor is assumed not related to the matrix suction with very important effect on the hydro-mechanical response occurring at local material points over unsaturated porous continua. The derived formulae of both generalized Biot effective stress and effective pressure (including effective Bishop parameter reflecting the isotropic effect of effective pressure) can be upscaled to a local material point, where the RVE is assigned, in macroscopic unsaturated porous continua, for computational multi-scale methods represented by the concurrent computational homogenization method for unsaturated granular materials.
-
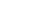
图 2参考颗粒
$k$ 表面$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^k$ 上由一个以绿色标记的干表面段$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{g}}}$ 隔开的以红色标记的两个相邻湿表面段$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{l}}}$ 和$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{k\left( {q + 1} \right){\text{l}}}$ Figure 2.Two neighboring wetted boundary segments
$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{l}}}$ and$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{k\left( {q + 1} \right){\text{l}}}$ marked with red color on the surface$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^k$ of the reference particlekisolated by a dry boundary segment$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{g}}}$ marked with green color on$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^k$ 图 3作用于第
$q$ 个双联液桥半月面与参考颗粒表面段$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{l}}}$ 两个交汇处的孔隙液相与气相之间的表面张力向量Tkq1和Tkq2Figure 3.Interfacial tension force vectors
${{\boldsymbol{T}}^{kq1}}$ and${{\boldsymbol{T}}^{kq2}}$ between pore liquid and gaseous phases applied at the two intersections formed by the liquid meniscus of theqth binary bond liquid bridge with the particle surface segment$\varGamma _{\text{s}}^{kq{\text{l}}}$ -
[1] Bishop AW. The principle of effective stress.Teknisk Ukeblad, 1959, 106(39): 859-863 [2] Skempton AW. Effective stress in soils, concrete and rock//Proc. Conf. on Pore Pressure and Suction in Soils, Butterworth, 1960: 4-16 [3] Bishop AW, Blight GE. Some aspects of effective stress in saturated and partly saturated soils.Geotechnique, 1963, 13: 177-197doi:10.1680/geot.1963.13.3.177 [4] Li XK, Zienkiewicz OC. Multiphase flow in deforming porous media and finite element solutions.Comput. Struct., 1992, 45: 211-227doi:10.1016/0045-7949(92)90405-O [5] Zienkiewicz OC, Chan AHC, Pastor M, et al. Computational Geomechanics with Special Reference to Earthquake Engineering. Chichester: Wiley, 1999 [6] Gray WG, Schrefler BA. Thermodynamic approach to effective stress in partially saturated porous media.Eur. J. Mech. A:Solids, 2001, 20: 521-538doi:10.1016/S0997-7538(01)01158-5 [7] Gray WG, Schrefler BA. Analysis of the solid phase stress tensor in multiphase porous media.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 2007, 31: 541-581 [8] Gray WG, Miller TC. Introduction to the Thermodynamically Constrained Averaging Theory for Porous Medium Systems. Switzerland: Springer, 2014 [9] 邵龙潭, 郭晓霞. 有效应力新解. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2014Shao Longtan, Guo Xiaoxia. New Insight on the Effective Stress. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2014 (in Chinese) [10] Auriault JL, Sanchez-Palencia E. Etude du comportement macroscopique d’un milieu poreux sature deformable.Journal de Mecanique, 1977, 16: 575-603 [11] Auriault JL. nonsaturated deformable porous media: quasistatics.Transport in Porous Media, 1987, 2: 45-64 [12] Nemat-Nasser S, Hori M. Micromechanics: Overall Properties of Heterogeneous Materials. Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1999 [13] Li XS. Effective stress in unsaturated soil: a microstructural analysis.Geotechnique, 2003, 53: 273-277doi:10.1680/geot.2003.53.2.273 [14] Lu N, Likos WJ. Suction stress characteristic curve for unsaturated soil.J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., 2006, 132: 131-142doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:2(131) [15] Hicher PY, Chang CS. A microstructural elastoplastic model for unsaturated granular materials.Int. J. Solids. Struct., 2007, 44: 2304-2323doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.07.007 [16] Hicher PY, Chang CS. Elastic model for partially saturated granular materials.J. Eng. Mech., 2008, 134: 505-513 [17] Scholtes L, Hicher PY, Nicot F, et al. On the capillary stress tensor in wet granular materials.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 2009, 33: 1289-1313doi:10.1002/nag.767 [18] Pierrat P, Caram HS. Tensile strength of wet granula materials.Powder Technology, 1997, 91: 83-93doi:10.1016/S0032-5910(96)03179-8 [19] Richefeu V, El Youssoufi MS, Peyroux R, et al. A model of capillary cohesion for numerical simulations of 3D polydisperse granular media.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 2008, 32: 1365-1383doi:10.1002/nag.674 [20] Than VD, Khamseh S, Tang AM, et al. Basic mechanical properties of wet granular materials: A DEM study.Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 143: C4016001 [21] Urso MED, Lawrence CJ, Adams MJ. Pendular funicular and capillary bridges: results for two dimensions.J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1999, 220: 42-56doi:10.1006/jcis.1999.6512 [22] El Shamy U, Groger T. Micromechanical aspects of the shear strength of wet granular soils.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 2008, 32: 1763-1790 [23] 杜友耀, 李锡夔. 二维液桥计算模型及湿颗粒材料离散元模拟. 计算力学学报, 2015, 32: 496-502 (Du Youyao, Li Xikui. 2D computational model of liquid bridge and DEM simulation of wet granular materials.Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2015, 32: 496-502 (in Chinese) [24] 李锡夔, 杜友耀, 段庆林. 基于介观结构的饱和与非饱和多孔介质有效应力. 力学学报, 2016, 48: 29-39 (Li Xikui, Du Youyao, Duan Qinglin. Meso-structure informed effective stresses in saturated and unsaturated porous media.Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2016, 48: 29-39 (in Chinese) [25] Li XK, Du YY, Zhang SG, et al. Meso-hydro-mechanically informed effective stresses and effective pressures for saturated and unsaturated porous media.European Journal of Mechanics A/Solids, 2016, 59: 24-36doi:10.1016/j.euromechsol.2016.03.005 [26] Oda M, Iwashita K. Mechanics of Granular Materials: An Introduction. Rotterdam: Balkema, 1999 [27] Walsh SDC, Tordesillas A, Peters JF. Development of micromechanical models for granular media: the projection problem.Granul Matter, 2007, 9: 337-352doi:10.1007/s10035-007-0043-5 [28] Li XK, Du YY, Duan QL. Micromechanically informed constitutive model and anisotropic damage characterization of cosserat continuum for granular materials.Int. J. Damage. Mech., 2013, 22: 643-682doi:10.1177/1056789512462427 [29] Zhang SG, Li XK, Du YY. A numerical model of discrete element-liquid bridge–liquid thin film system for wet deforming granular medium at low saturation.Powder Technology, 2022, 399: 117217doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117217 [30] Souli´e, F, Cherblanc F, El Youssoufi MS, et al. Influence of liquid bridges on the mechanical behaviour of polydisperse granular materials.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 2006, 30: 213-228 [31] Li XK, Zhang SG, Duan QL. Second-order concurrent computational homogenization method and multi-scale hydro-mechanical modeling for saturated granular materials.Int. J. for Multiscale Computational Engineering, 2020, 18: 199-240doi:10.1615/IntJMultCompEng.2020031587 [32] Li XK, Zhang X, Zhang JB. A generalized Hill’s lemma and micromechanically based macroscopic constitutive model for heterogeneous granular materials.Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199: 3137-3152doi:10.1016/j.cma.2010.06.016 [33] Li XK, Zienkiewicz OC, Xie YM. A numerical model for immiscible two-phase fluid flow in a porous medium and its time domain solution.Int. J. for Numerical Methods in Eng., 1990, 30: 1195-1212doi:10.1002/nme.1620300608 [34] Schrefler BA, Zhan XY. A fully coupled model for water flow and airflow in deformable porous media.Water Resour Res., 1993, 29: 155-167doi:10.1029/92WR01737 [35] Lewis RW, Schrefler BA. The Finite Element Method in the Static and Dynamic Deformation and Consolidation of Porous Media. Second Edition. England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1998: 1-492 [36] Fredlund DG, Rahardjo H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1993: 1-517 [37] 沈珠江. 理论土力学. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2000Shen Zhujiang. Theoretical Soil Mechanics. Beijing: China Water Power Press, 2000 (in Chinese) [38] Zienkiewicz OC, Shiomi T. Dynamic behavior of saturated porous media:the generalized Boit formulation and its numerical solution.Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech., 1984, 8: 71-96 -





 下载:
下载: