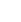STUDY ON THE BEHAVIOR OF BUBBLES COLLIDING WITH HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC CURVED WALLS
-
摘要:气泡碰撞固壁行为和影响因素的研究一直以来都是科学界关注的重点之一, 其在矿物浮选、气膜减阻等工业领域中的应用也极具科研价值. 论文聚焦曲壁对于气泡撞击行为特性的影响研究. 采用高速摄像技术记录气泡碰撞不同曲率半径下亲疏水曲壁的撞击过程, 分析了曲壁润湿性、曲率半径对气泡碰撞固体曲壁的影响规律. 结果表明, 气泡碰撞亲水曲壁时会发生多次弹跳直至离开曲壁; 曲率半径越大, 弹跳次数越少, 且第一次反弹的最远距离越近, 再次发生碰壁时的速度越小. 而碰撞疏水曲壁时会出现碰撞−滑移−附着的现象, 此外针对液膜挤压破裂的现象, 建立理论模型推导出液膜诱导时间的预测公式, 其主要与液膜厚度、液膜临界破裂厚度和液膜被压缩速度有关, 预测误差小于5.0%.Abstract:The research on the behavior and influencing factors of bubble collision has always been one of the focuses of scientific circles. Its application in industrial fields such as mineral flotation and gas film drag reduction is also of great scientific research value. This paper focuses on the influence of curved wall on bubble impact behavior. The impact process of bubbles colliding with hydrophilic and hydrophobic curved wall under different radius of curvature was recorded by high-speed camera technology, and the effects of wettability and radius of curvature of curved wall on bubbles colliding with solid curved wall were analyzed. The results show that when the bubble collides with the hydrophilic curved wall, it will bounce many times until it leaves the curved wall; The larger the radius of curvature, the less the number of jumps, and the closer the farthest distance of the first rebound, the smaller the speed of hitting the wall again. In addition, aiming at the phenomenon of liquid film extrusion rupture, a theoretical model is established to deduce the prediction formula of liquid film induction time, which is mainly related to the thickness of liquid film, the critical rupture thickness of liquid film and the compression speed of liquid film, and the prediction error is less than 5.0%.
-
Key words:
- bubble/
- wettability/
- collision/
- film induction time
-
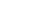
图 1气泡撞击曲壁实验装置图
(a) 1气泡发生器; 2微量注射泵; 3 LED平板灯; 4高速摄像机; 5计算机;6实验曲壁; 7水箱; 8支架. (b)实验曲壁二维局部放大图
Figure 1.Diagram of the experimental device of bubble impact on curved wall
(a) 1 Bubble generator; 2 micro syringe pump; 3 LED flat panel lamp; 4 high-speed camera; 5 computer; 6 experimental curved wall; 7 water tank; 8 stand. (b) Two-dimensional partial magnification of the experimental curved wall
-
[1] 周欣, 宋宝华, 王中原等. 基于气泡碰撞的筛板曝气试验研究. 环境工程, 2013(S1): 426-429Zhou Xin, Song Baohua, Wang Zhongyuan, et al. Study of aeration experiment with sieve based on bubble collision.Environmental Engineering, 2013(S1): 426-429(in Chinese)) [2] 王静超, 马军, 刘芳. 气浮接触区气泡-颗粒碰撞效率影响因素分析. 工业水处理, 2008, 28(9): 66-69doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2008.09.020Wang Jingchao, Ma Jun, Liu Fang. Influential factor analysis of the bubble-particle collision efficiency in the contactzone of dissolved air flotation.Industrial Water Treatment, 2008, 28(9): 66-69 (in Chinese))doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2008.09.020 [3] Hassanzadeh A, Hassas BV, Kouachi S, et al. Effect of bubble size and velocity on collision efficiency in chalcopyrite flotation.Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 498: 258-267 [4] Murai Y. Frictional drag reduction by bubble injection.Experiments in Fluids, 2014, 55(7): 1-28 [5] Tsao HK, Koch DL. Observations of high Reynolds number bubbles interacting with a rigid wall.Physics of Fluids, 1997, 9(1): 44-56doi:10.1063/1.869168 [6] Legendre D, Daniel C, Guiraud P. Experimental study of a drop bouncing on a wall in a liquid.Physics of Fluids, 2005, 17(9): 097105doi:10.1063/1.2010527 [7] Krzan M, Zawala J, Malysa K. Development of steady state adsorption distribution over interface of a bubble rising in solutions of n-alkanols (C5, C8) and n-alkyltrimethylammonium bromides (C8, C12, C16).Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 298(1-2): 42-51 [8] Zhang C, Li J, Luo LS, et al. Numerical simulation for a rising bubble interacting with a solid wall: Impact, bounce, and thin film dynamics.Physics of Fluids, 2018, 30(11): 112106doi:10.1063/1.5055671 [9] Qin T, Ragab S, Yue P. Axisymmetric simulation of the interaction of a rising bubble with a rigid surface in viscous flow.International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 52: 60-70doi:10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2013.01.001 [10] Hendrix MHW, Manica R, Klaseboer E, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of thin liquid films during impact of water bubbles on glass on a micrometer to nanometer scale.Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(24): 247803doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.247803 [11] Zhang X, Tchoukov P, Manica R, et al. Simultaneous measurement of dynamic force and spatial thin film thickness between deformable and solid surfaces by integrated thin liquid film force apparatus.Soft Matter, 2016, 12(44): 9105-9114doi:10.1039/C6SM02067D [12] Liu B, Manica R, Zhang XR, et al. Dynamic interaction between a millimeter-sized bubble and surface microbubbles in water.Langmuir, 2018, 34(39): 11667-11675doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01202 [13] Klaseboer E, Chevaillier JP, Maté A, et al. Model and experiments of a drop impinging on an immersed wall.Physics of Fluids, 2001, 13(1): 45-57doi:10.1063/1.1331313 [14] Klaseboer E, Manica R, Hendrix MHW, et al. A force balance model for the motion, impact, and bounce of bubbles.Physics of Fluids, 2014, 26(9): 092101doi:10.1063/1.4894067 [15] Zenit R, Legendre D. The coefficient of restitution for air bubbles colliding against solid walls in viscous liquids.Physics of Fluids, 2009, 21(8): 083306doi:10.1063/1.3210764 [16] Wang L, Sharp D, Masliyah J, et al. Measurement of interactions between solid particles, liquid droplets, and/or gas bubbles in a liquid using an integrated thin film drainage apparatus.Langmuir, 2013, 29(11): 3594-3603doi:10.1021/la304490e [17] Zawala J, Dabros T. Analysis of energy balance during collision of an air bubble with a solid wall.Physics of Fluids, 2013, 25(12): 123101doi:10.1063/1.4847015 [18] Krasowska M, Malysa K. Kinetics of bubble collision and attachment to hydrophobic solids: I. Effect of surface roughness.International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2007, 81(4): 205-216doi:10.1016/j.minpro.2006.05.003 [19] Kosior D, Zawala J, Niecikowska A, et al. Influence of non-ionic and ionic surfactants on kinetics of the bubble attachment to hydrophilic and hydrophobic solids.Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 470: 333-341 [20] Kosior D, Zawala J, Malysa K. Influence of n-octanol on the bubble impact velocity, bouncing and the three phase contact formation at hydrophobic solid surfaces.Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 441: 788-795doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.10.025 [21] Zawala J, Krasowaka M, Dabros T, et al. Influence of bubble kinetic energy on its bouncing during collisions with various interfaces.Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2007, 85(5): 669-678 [22] Reynolds O. On the theory of lubrication and its application to Mr. Beauchamp Tower's experiments, including an experimental determination of the viscosity of olive oil.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc., 1885, 1: 157 [23] Stöckelhuber KW, Radoev B, Wenger A, et al. Rupture of wetting films caused by nanobubbles.Langmuir, 2004, 20(1): 164-168doi:10.1021/la0354887 [24] Schulze HJ, Stockelhuber KW, Wenger A. The influence of acting forces on the rupture mechanism of wetting films-nucleation or capillary waves.Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2001, 192(1-3): 61-72 [25] Emery TS, Kandlikar SG. Film size during bubble collision with a solid surface.Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2019, 141(7). [26] Gu G, Xu Z, Nandakumar K, et al. Effects of physical environment on induction time of ai-bitumen attachment.International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2003, 69(1-4): 235-250doi:10.1016/S0301-7516(02)00128-X [27] Albijanic B, Ozdemir O, Nguyen AV, et al. A review of induction and attachment times of wetting thin films between air bubbles and particles and its relevance in the separation of particles by flotation.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 159(1): 1-21doi:10.1016/j.cis.2010.04.003 [28] Manica R, Klaseboer E, Chan DYC. The hydrodynamics of bubble rise and impact with solid surfaces.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 235: 214-232doi:10.1016/j.cis.2016.06.010 [29] 罗松, 于勇. 气泡碰壁受力模型和反弹规律. 气体物理, 2019, 4(2): 30-43Luo Song, Yu Yong. Force model and rebound law of bubble hitting wall.Physics of Gases, 2019, 4(2): 30-43(in Chinese)) [30] Chan DYC, Klaseboer E, Manica R. Film drainage and coalescence between deformable drops and bubbles.Soft Matter, 2011, 7(6): 2235-2264doi:10.1039/C0SM00812E [31] Vinogradova OI. Drainage of a thin liquid film confined between hydrophobic surfaces.Langmuir, 1995, 11(6): 2213-2220doi:10.1021/la00006a059 [32] Leal LG. Advanced Transport Phenomena: Fluid Mechanics and Convective Transport Processes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007 [33] Wang W, Zhou Z, Nandakumar K, et al. An induction time model for the attachment of an air bubble to a hydrophobic sphere in aqueous solutions.International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 75(1-2): 69-82doi:10.1016/j.minpro.2004.04.009 [34] Reuter F, Kaiser SA. High-speed film-thickness measurements between a collapsing cavitation bubble and a solid surface with total internal reflection shadowmetry.Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(9): 097108doi:10.1063/1.5095148 -





 下载:
下载: